UX Design (User Experience) is fundamentally about creating experiences that are not just intuitive and engaging but also genuinely fulfilling for the user. This involves a detailed and thoughtful process of designing products, whether they are websites or mobile applications, to be user-friendly, accessible, and a delight to use.
Effective UX design plays a pivotal role in boosting user satisfaction, fostering engagement, and enhancing the overall performance of a digital product.
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) Design is an approach in the field of design that focuses on the end-user's interaction with a company, its services, and its products. The primary goal of UX design is to create easy, efficient, relevant, and all-around pleasant experiences for the user. It's about building the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function.
Core Principles of UX Design
- User-Centricity
At the heart of UX design lies the principle of designing for the user’s needs, preferences, and experiences. - Usability
The ease with which your users can navigate your product is paramount. This involves intuitive design, clear navigation, and minimal user effort. - Accessibility
Ensuring that your digital product is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. - Desirability
The design should evoke emotions and appreciation, creating a connection between the user and the product. - Value
Beyond just functional, the design should provide value by solving real problems and enhancing the user’s life or work.
With a vast array of options available to consumers, the quality of the user experience can set a product apart. It not only improves user satisfaction but also helps in building brand loyalty and trust. By prioritizing the user's needs and preferences, businesses can create more meaningful and successful interactions in the digital space.
UX vs UI: Understanding the Differences
While UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) are closely related, they are distinct aspects of the design process.
UI Design refers to the aesthetic elements through which people interact with a product. This includes the colour scheme, typography, and layout. Essentially, UI is all about the look and feel of the product interface.
In contrast, UX Design is about the overall feel of the experience. It's more about the functionality and usability of the product than its visual aspects. While UI focuses on the specific interface elements, UX takes a broader, more holistic view of the entire user's journey with the product.
Understanding the differences between UX and UI is crucial as they work hand in hand. A stunning interface (UI) might attract users initially, but it's the overall experience (UX) that keeps them returning. An ideal digital product combines an excellent UI with an equally impressive UX, ensuring not only that the product looks appealing but also that it provides a seamless and satisfying user experience.
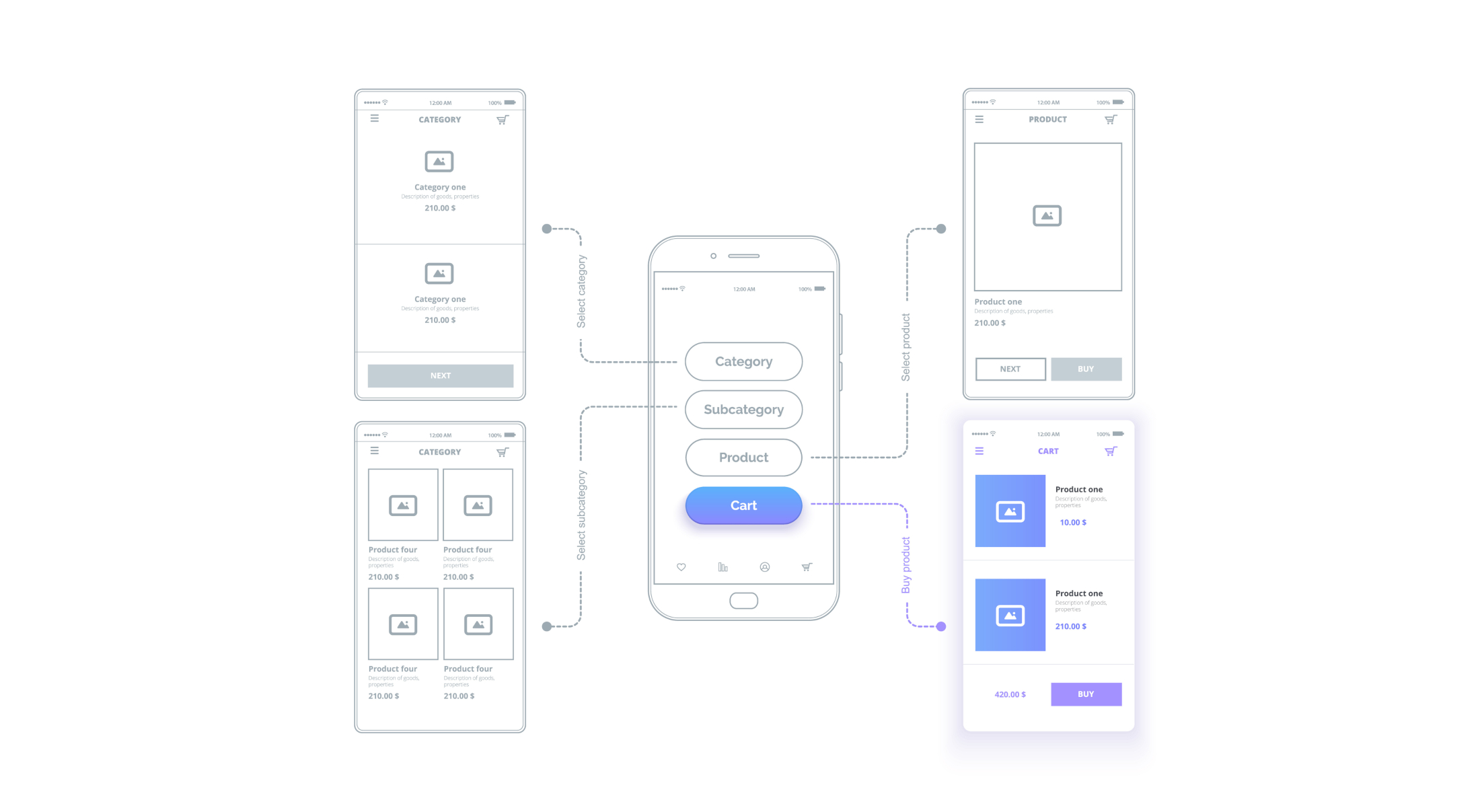
UX Design in Websites and Mobile Apps
UX Design plays a role in shaping the user experience across various platforms, particularly in websites and mobile apps. While the core principles of UX Design apply universally, the approach must be tailored to fit the unique requirements of each platform.
Web UX Design
- Navigation and Content Hierarchy
Web UX places a strong emphasis on intuitive navigation and well-structured content. Users should find what they're looking for effortlessly. - Responsive Design
A great web UX adapts to various screen sizes and devices, offering a consistent experience across desktops, tablets, and mobile phones. - Load Times and Performance
Fast loading times and smooth performance are crucial for a positive web user experience. - Accessibility
Ensuring that web experiences are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is a key aspect of web UX.
Mobile App UX Design
- Touch Interactions
Unlike websites, mobile apps need to account for touch interactions, including swipes and taps. - Limited Screen Real Estate
Mobile UX must prioritize key features and content due to smaller screen sizes. - Context of Use
Mobile apps are often used on the go, so designs should facilitate quick and efficient interactions. - Hardware Integration
Mobile UX can leverage device capabilities like cameras, GPS, and accelerometers for a richer user experience.
A website with a clean layout, intuitive navigation, and responsive design that adjusts to different screen sizes seamlessly.
A mobile app with a simple, gesture-based interface that allows users to complete tasks quickly and efficiently, integrating well with the device's hardware features.
Case Studies of Successful UX Designs
Airbnb (Web and Mobile App)
Airbnb's platform is a prime example of excellent UX design. On both web and mobile, Airbnb offers a seamless booking experience, with intuitive search filters, clear listings, and an easy booking process. Their attention to visual aesthetics, combined with user-friendly functionality, makes for a satisfying user experience.
Spotify (Mobile App)
Spotify's mobile app excels in providing a personalized music experience. Its easy navigation, coupled with AI-driven music recommendations, ensures users find exactly what they're looking for. The app's use of swipe gestures and integration with various devices highlights its superior mobile UX design.
Dropbox (Web)
Dropbox’s website is noted for its simplicity and ease of use. The design focuses on clarity and efficiency, making file storage and sharing straightforward for users. The website's responsive design ensures a consistent experience across various devices.
UX Design Process and Methods
The UX design process is a systematic approach that ensures the end product resonates well with its intended users. It involves several stages, each focusing on different aspects of the design, from understanding user needs to refining the product based on feedback.
Overview of the UX Design Process
- Research
This initial stage involves understanding the users, their needs, behaviours, and motivations. Methods include surveys, interviews, and market analysis. - Design
Based on the research, designers create wireframes, mockups, and prototypes. This stage involves sketching, ideation, and conceptualization. - Testing
The prototypes are tested with real users to gather feedback. This stage helps identify usability issues and areas for improvement. - Implementation
The final design is developed and launched. However, UX design is an ongoing process, and the product will continue to evolve based on user feedback and changing needs.
Key Methods and Tools in UX Design
- Wireframing and Prototyping Tools
Software like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma helps in creating the visual blueprint of the product. - User Testing Platforms
Tools like Lyssna (previously UsabilityHub) and UserTesting provide platforms to gather feedback from actual users. - Analytics and Feedback Tools
Google Analytics, Hotjar, and similar tools help in understanding user interactions and behaviours on the live product.
Iterative Design and Prototyping
A fundamental aspect of UX design is the iterative process, which involves repeated cycles of designing, testing, and refining the product. This approach ensures that the product evolves based on actual user feedback and real-world usage, rather than assumptions.
Prototyping is a crucial part of this iterative process. It involves creating a simplified version of the product, which can be a paper model, a digital mockup, or a fully interactive simulation. Prototypes are essential for visualizing and testing design concepts without the need for full development.
The iterative design and prototyping phase can be summarized as follows:
- Create: Design a prototype based on initial research and design thinking.
- Test: Use the prototype in user testing to gather feedback on usability and user experience.
- Learn: Analyze the feedback to identify what works and what doesn’t.
- Refine: Make necessary changes and improvements to the design.
- Repeat: Go through the cycle again with the updated prototype, refining the product until it meets the desired user experience standards.
This iterative process of design and prototyping is vital in creating products that truly meet user needs and expectations. It allows for flexibility and continuous improvement, ensuring the final product is not only functional but also highly user-centric.
User Research in UX Design
User research is a cornerstone of UX design, as it provides the insights needed to create products that resonate with the target audience. The importance of this research cannot be overstated—it is what grounds the design process in reality and ensures that the final product truly meets the needs and expectations of its users.
Importance of User Research
User research is an indispensable component of UX design, as it plays a critical role in accurately identifying user needs. By understanding what users truly need, rather than relying on assumptions, designers can create products that are much more aligned with user expectations.
This research is instrumental in guiding design decisions, ensuring that every aspect of the product is informed by genuine user insights. Consequently, products developed with direct input from user research are more likely to resonate with the target audience, leading to enhanced user satisfaction.
Incorporating this feedback into the design process is not just a best practice; it's a vital step in creating digital products that successfully engage and satisfy users.
Common User Research Methods
- Surveys and Questionnaires
These tools can gather a large amount of data from a wide audience quickly. - Interviews
One-on-one discussions provide deep insights into user motivations, behaviors, and attitudes. - User Testing
Observing users interacting with a product or prototype can unveil usability issues and areas for improvement. - Ethnographic Research
This involves observing users in their natural environment to understand how they interact with a product in real-life scenarios. - Persona Development
Creating detailed profiles of typical users can help in visualizing the target audience throughout the design process.
Analyzing User Feedback and Data
The analysis of user feedback and data is a critical step in the UX design process. It involves interpreting the information gathered from various research methods and translating it into actionable insights.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends
Look for common themes in user feedback that can highlight strengths and weaknesses in the design. - User Pain Points
Pinpoint specific areas where users struggle and focus on addressing these issues. - Feedback Implementation
Determine how to best incorporate the feedback into the design. This may involve prioritizing certain changes based on their potential impact. - Continuous Improvement
User feedback should not be viewed as a one-time checkpoint but as an ongoing resource for continuous product refinement.
Utilizing tools like analytics platforms, heat maps, and A/B testing can also provide quantitative data that complements the qualitative insights from direct user feedback. This blend of data helps create a comprehensive understanding of user needs and preferences, forming a solid foundation for creating a user-centric design.
Best Practices in UX Design
In UX design, adhering to best practices is key to creating an engaging and effective user experience. These practices are guidelines that help designers focus on creating products that are not only visually appealing but also functional and user-friendly. Below is a list of essential best practices in UX design:
- Focus on User-Centricity
- Simplicity is Key
- Consistency Across the Design
- Clear and Intuitive Navigation
- Fast Load Times
- Responsive Design
- Conduct Regular Testing
- Use Familiar UI Elements
- Provide Helpful Feedback
In addition to these best practices, incorporating accessibility and inclusivity into UX design is not just a best practice; it's a crucial aspect of creating products that are genuinely user-centric. Ensuring that digital products are accessible to people with a wide range of abilities is key. This means considering the needs of individuals with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments.
Practical steps include using alt text for images, providing keyboard navigation, and ensuring adequate colour contrast to cater to users with different needs.
Additionally, acknowledging and catering to a diverse audience is fundamental. This encompasses being mindful of cultural sensitivities, offering language options, and ensuring that content and imagery are inclusive and do not inadvertently exclude any groups.
By adhering to these practices, UX designers enhance not only the user experience but also the overall success of the product. Prioritizing inclusivity, along with user-centricity and simplicity, enables the creation of digital products that resonate with a diverse audience and excel in the competitive digital environment.
Challenges in UX Design and Solutions
While UX design is a field full of creativity and innovation, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and knowing how to address them is crucial for any UX designer aiming to create effective and user-friendly designs.
Challenge: Balancing User Needs and Business Goals
One of the primary challenges in UX design is finding the right balance between user expectations and business objectives. This often involves navigating a delicate tension to ensure that the needs of both parties are effectively met.
Solution: To address this, it's essential to align user needs with business goals. Engaging in stakeholder interviews and closely aligning the UX strategy with business objectives can be highly effective. The goal is to find a middle ground that satisfies both users and the business, ensuring a mutually beneficial outcome.
Challenge: Designing for Diverse User Groups
UX designers often face the task of creating designs that appeal to a wide range of users, each with their own preferences, abilities, and backgrounds. This diversity presents a significant challenge in ensuring the design is universally appealing and accessible.
Solution: Adopting an inclusive design approach is key. This involves creating personas for different user types and conducting extensive user testing to ensure the design is accommodating and accessible to all, regardless of their unique characteristics.
Challenge: Keeping Up with Technological Advances
The rapid pace of technological change means UX designers must continuously adapt and update their skills and methodologies to stay relevant and effective.
Solution: Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial. Regularly updating skills through training, workshops, and webinars helps designers stay current with the latest trends and technologies in UX design.
Challenge: Dealing with Limited Resources
Time, budget, and manpower constraints can significantly restrict the scope and depth of UX projects, making it challenging to achieve desired outcomes.
Solution: Efficient resource management is essential. Prioritizing tasks based on their impact and available resources, and employing agile methodologies, can help manage projects effectively within these constraints.
Challenge: Ensuring Consistency Across Different Platforms
Creating a uniform user experience across various devices and platforms is a challenging task, requiring a consistent approach to design.
Solution: Developing a unified design system is critical. This system should guide the design process across different platforms and devices to maintain a cohesive and consistent user experience.
Challenge: Gathering and Incorporating User Feedback
Effectively collecting and integrating user feedback into the design process can be complex and time-consuming but is essential for creating user-centered designs.
Solution: Implementing efficient feedback mechanisms is key. Using tools and methods like user surveys, A/B testing, and usability studies can streamline the process of gathering and analyzing user feedback, making it easier to incorporate into the design.
Charting the Future of Digital Experiences
From the fundamental principles and processes to best practices and overcoming challenges, it's clear that UX design is not just about creating aesthetically pleasing interfaces; it's about crafting user-centric experiences that are intuitive, inclusive, and engaging.
The role of UX design in enhancing the effectiveness and appeal of websites and mobile applications cannot be understated.
If you're ready to elevate your UX design and transform your digital products, e-dimensionz is here to help. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to bringing your vision to life, ensuring that your web and mobile applications are not only visually stunning but also user-centric and intuitive.
Contact e-dimensionz for a quote, and let's work together to turn your UX design aspirations into reality. A well-executed UX strategy can be the difference between a product that merely functions and one that thrives by delivering exceptional user experiences.